(Development version for reference; code functions now in R/gp_mcmc.R)
Function definitions
library(mcmc)
#' Basic regression in Gaussian processes
#'
#'
#' @param x Observed x values, (vector or matrix with columns for each dimension of data)
#' @param y Vector of observed y values in the training data
#' @param init_pars the initial guesses for lengthscale l and process noise sigma_n
#' @param n iterations of the metropolis algorithm
#' @details Currently assumes the covariance function. By default we will use
#' the squared exponential (also called radial basis or Gaussian,
#' though it is not this that gives Gaussian process it's name;
#' any covariance function would do) as the covariance function,
#' $\operatorname{cov}(X_i, X_j) = \exp\left(-\frac{(X_i - X_j)^2}{2 \ell ^ 2}\right)$
#' @return the MCMC output, as constructed by \link{metrop} from the mcmc package.
#' @export
#' @import mcmc
gp_mcmc <- function(x, y, init_pars = c(l=1, sigma.n=1), n = 1e4, d.p = c(5,5), s2.p = c(5,5)){
lpriors <- function(pars){
prior <- unname(
dgamma(exp(pars[1]), d.p[1], scale = d.p[2]) *
dgamma(exp(pars[2]), s2.p[1], s2.p[2])
)
log(prior)
}
posterior <- function(pars, x, y){
l <- exp(pars[1])
sigma.n <- exp(pars[2])
cov <- function(X, Y) outer(X, Y, SE, l)
I <- diag(1, length(x))
K <- cov(x, x)
loglik <- - 0.5 * t(y) %*% solve(K + sigma.n^2 * I) %*% y -
log(det(K + sigma.n^2*I)) -
length(y) * log(2 * pi) / 2
loglik + lpriors(pars)
}
out <- metrop(posterior, log(init_pars), n, x = obs$x, y = obs$y)
out$d.p <- d.p
out$s2.p <- s2.p
out
}#' predict the expected values and posterior distributions of the Gaussian Process
#'
#' @param x_predict the values at which we desire predictions
#' @param covs if TRUE, return covariances instead of variances (set high thinning as this is memory intensive)
#' @import reshape2
#' @export
gp_predict <- function(gp, x_predict, burnin=0, thin=1, covs=FALSE){
postdist <- cbind(index=1:gp$nbatch, as.data.frame(exp(gp$batch)))
s <- seq(burnin+1, gp$nbatch, by=thin)
postdist <- postdist[s,]
names(postdist) <- c("index", names(gp$initial))
indices <- 1:dim(postdist)[1]
out <- lapply(indices, function(i){
l <- postdist[i, "l"]
sigma.n <- postdist[i, "sigma.n"]
cov <- function(X, Y) outer(X, Y, SE, l)
cov_xx_inv <- solve(cov(obs$x, obs$x) + sigma.n^2 * diag(1, length(obs$x)))
Ef <- cov(x_predict, obs$x) %*% cov_xx_inv %*% obs$y
Cf <- cov(x_predict, x_predict) - cov(x_predict, obs$x) %*% cov_xx_inv %*% cov(obs$x, x_predict)
list(Ef = Ef, Cf = Cf, Vf = diag(Cf))
})
Ef_posterior <- sapply(out, `[[`, "Ef")
Cf_posterior <- sapply(out, `[[`, "Cf")
Vf_posterior <- sapply(out, `[[`, "Vf")
E_Ef <- rowMeans(Ef_posterior)
E_Cf <- matrix( apply(Cf_posterior, 1, sum) / dim(Cf_posterior)[2], ncol = sqrt(dim(Cf_posterior)[1]) )
E_Vf <- diag(E_Cf) # same as rowMeans(Vf_posterior)
# list format better for return
Cf_posterior <- lapply(out, `[[`, "Cf")
list(Ef_posterior = Ef_posterior,
Vf_posterior = Vf_posterior,
Cf_posterior = Cf_posterior,
E_Ef = E_Ef, E_Cf = E_Cf, E_Vf = E_Vf)
} library(reshape2)
library(ggplot2)
library(plyr)
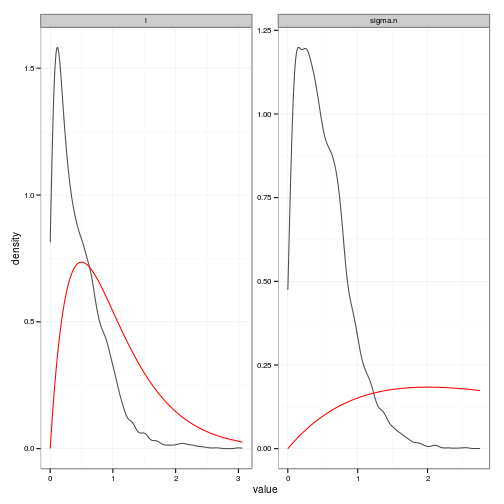
#' Summary plots showing the trace and posteriors for the gp_mcmc estimates
#'
#' @param gp a fit of the gaussian process from gp_mcmc
#' @param burnin length of sequence to discard as a transient
#' @param thin frequency of sub-sampling (make posterior distribution smaller if necessary)
#' @return two ggplot2 objects, one plotting the trace and one
#' plotting the posteriors in black with priors overlaid in red.
#' @import reshape2
#' @import ggplot2
#' @import plyr
#' @export
summary_gp_mcmc <- function(gp, burnin=0, thin=1){
postdist <- cbind(index=1:gp$nbatch, as.data.frame(exp(gp$batch)))
s <- seq(burnin+1, gp$nbatch, by=thin)
postdist <- postdist[s,]
names(postdist) <- c("index", names(gp$initial))
# TRACES
df <- melt(postdist, id="index")
traces_plot <-
ggplot(df) + geom_line(aes(index, value)) +
facet_wrap(~ variable, scale="free", ncol=1)
s2.p <- gp$s2.p
d.p <- gp$d.p
s2_prior <- function(x) dgamma(x, s2.p[1], s2.p[2])
d_prior <- function(x) dgamma(x, d.p[1], scale = d.p[2])
prior_fns <- list(l = d_prior, sigma.n = s2_prior)
prior_curves <- ddply(df, "variable", function(dd){
grid <- seq(min(dd$value), max(dd$value), length = 100)
data.frame(value = grid, density = prior_fns[[dd$variable[1]]](grid))
})
# Posteriors (easier to read than histograms)
posteriors_plot <- ggplot(df, aes(value)) +
stat_density(geom="path", position="identity", alpha=0.7) +
geom_line(data=prior_curves, aes(x=value, y=density), col="red") +
facet_wrap(~ variable, scale="free", ncol=2)
print(traces_plot)
print(posteriors_plot)
out <- list(traces_plot = traces_plot, posteriors_plot = posteriors_plot)
invisible(out)
}
# Helper function: The default covariance function
SE <- function(Xi,Xj, l) exp(-0.5 * (Xi - Xj) ^ 2 / l ^ 2)Example
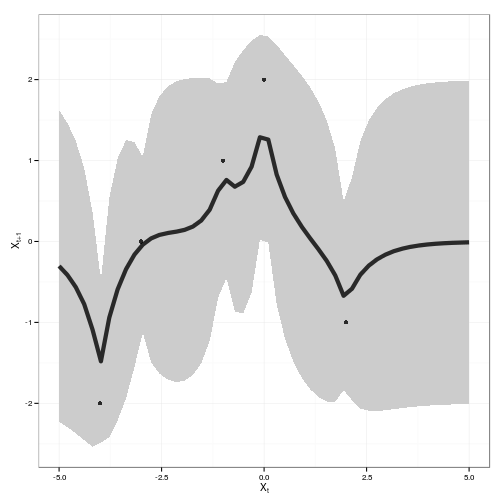
x_predict <- seq(-5,5,len=50)
obs <- data.frame(x = c(-4, -3, -1, 0, 2),
y = c(-2, 0, 1, 2, -1))gp <- gp_mcmc(obs$x, obs$y, d.p = c(2,.5), s2.p = c(2,.5))summary_gp_mcmc(gp)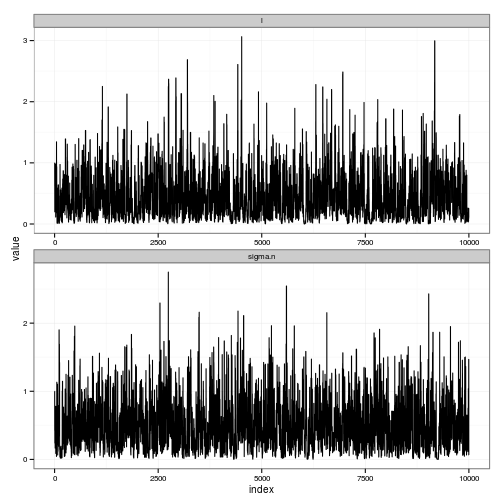
gp_dat <- gp_predict(gp, x_predict)tgp_dat <-
data.frame( x = x_predict,
y = gp_dat$E_Ef,
ymin = gp_dat$E_Ef - 2 * sqrt(gp_dat$E_Vf),
ymax = gp_dat$E_Ef + 2 * sqrt(gp_dat$E_Vf) )
ggplot(tgp_dat) + geom_ribbon(aes(x,y,ymin=ymin,ymax=ymax), fill="gray80") +
geom_line(aes(x, y), lwd=2, alpha=0.8) +
geom_point(data=obs, aes(x,y), alpha=0.8) +
xlab(expression(X[t])) + ylab(expression(X[t+1]))